Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
As the world grapples with the consequences of climate change, scientists are uncovering new and unexpected effects of rising temperatures and changing environmental conditions. One such consequence is the potential worsening spread of ocean noise, which can have significant implications for marine life. Researchers have found that climate change can influence how sound travels through water, leading to increased noise levels in certain areas of the world’s oceans.
Human activity has long been recognized as a major contributor to ocean noise pollution. From the rumble of boats to the din of oil drilling, sounds generated by human activities can travel across vast distances in the oceans, affecting marine creatures. With the increasing global demand for goods and the subsequent rise in shipping activities, the volume of noise in the oceans has been on the rise. As more goods are bought and shipped, the noise generated by these activities intensifies, creating a cacophony that can disrupt the natural acoustic environment of marine ecosystems.
While the impact of human activity on ocean noise has been well-documented, researchers are now exploring the role of climate change in exacerbating this issue. Climate change is altering various environmental factors in the oceans, including temperature, salt levels, and acidity. These changes can have significant implications for how sound travels through water.
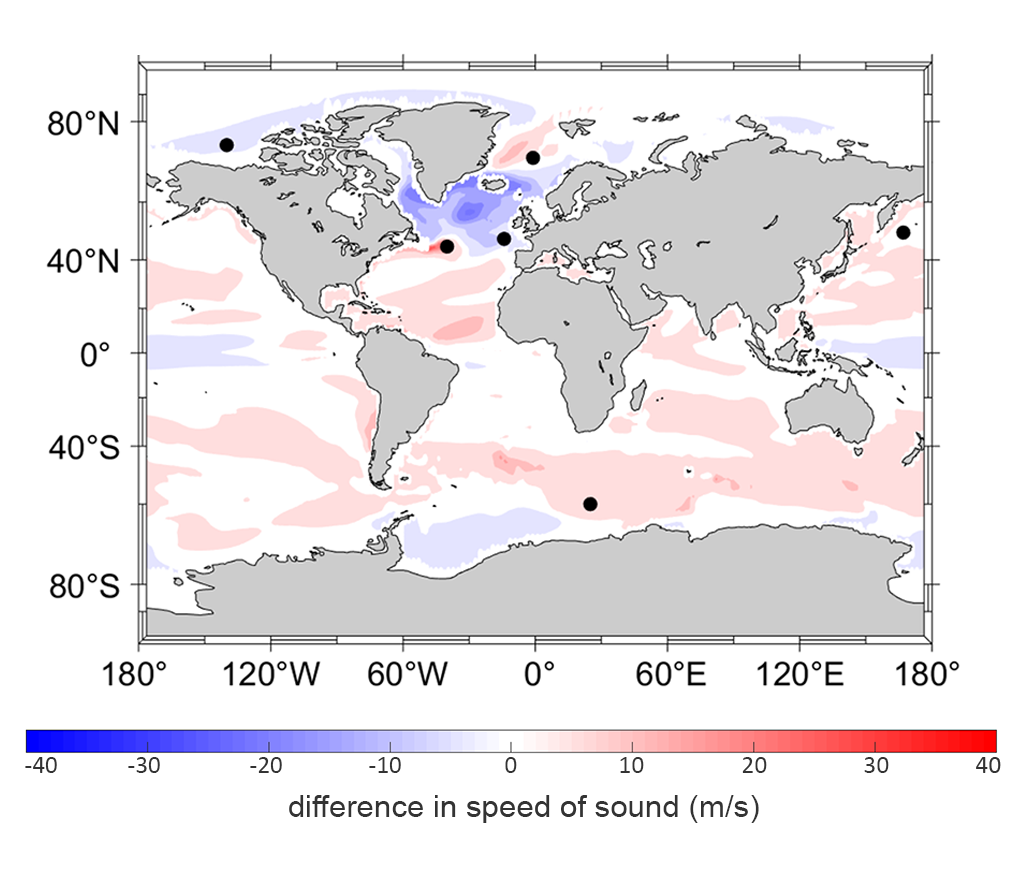
Scientists at the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research have used computer models to simulate the effects of climate change on sound propagation in the world’s oceans. They found that as waters become more acidic, they become less capable of absorbing sound at certain wavelengths. This allows sounds to travel further, contributing to the overall noise levels in specific areas.
Furthermore, changes in temperature and salt levels can impact the mixing of different layers of the ocean. This, in turn, affects how sound waves propagate through the water. The researchers discovered that the melting of ice off Greenland in the North Atlantic has led to a boost in sound levels in the upper 125 meters of the ocean. Sound waves tend to bend towards the coldest areas, and as a result, they get trapped in the chilly top layer of water, spreading further across the water instead of traveling deeper.
The increased spread of ocean noise due to climate change can have detrimental effects on marine life. Many marine animals rely on sound for communication, hunting, and navigation. The excessive noise can disrupt these crucial activities, leading to stress and potential harm to these species.
Marine mammals, such as whales and dolphins, are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of ocean noise. They use sound to communicate with each other over long distances and navigate their environments. The increased noise levels can interfere with their ability to detect important signals and disrupt their natural behaviors. For example, marine mammals may avoid certain areas, such as harbors, where noise levels are high, impacting their feeding and breeding patterns.
Furthermore, the North Atlantic, which experiences a significant increase in noise levels due to climate change, is a crucial route for ship traffic between Europe and North America. The noise generated by this activity could further contribute to the already noisy environment, potentially causing additional stress to marine life in the region.
The findings of this research highlight the urgent need for further study and mitigation strategies to address the impact of climate change on ocean noise. Understanding the complex interactions between climate change, human activity, and sound propagation in the oceans is crucial for developing effective measures to protect marine ecosystems.
Efforts to reduce noise pollution, such as implementing quieter ship designs and regulating shipping routes, can help mitigate the negative effects on marine life. Additionally, addressing the root causes of climate change through reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources is essential for minimizing the broader impacts on the world’s oceans.
By recognizing the connection between climate change and the spread of ocean noise, we can work towards preserving the acoustic integrity of marine ecosystems and ensuring the well-being of the diverse species that call the oceans their home.
The worsening spread of ocean noise due to climate change can have significant effects on marine life and ecosystems. The increased noise levels in the oceans can disrupt the natural behaviors and vital activities of various marine species, leading to potential harm and ecological consequences.
Marine animals heavily rely on sound for communication, navigation, and finding food. The excessive noise generated by human activities and amplified by climate change can interfere with these crucial functions. Whales, dolphins, and other marine mammals use intricate vocalizations to communicate with each other over long distances. The increased noise levels can mask these important signals, making it challenging for these animals to effectively communicate and coordinate their behaviors.
Furthermore, noise pollution can disrupt the navigation abilities of marine species. Many animals, such as sea turtles and migratory fish, rely on sound cues to navigate during their long-distance migrations. The excessive noise can confuse these animals, leading to disorientation and potential stranding or migration errors.
The spread of ocean noise can also have detrimental effects on the feeding and hunting behaviors of marine organisms. Many species, including marine mammals, rely on sound to locate and capture their prey. The increased noise levels can mask the sounds produced by their prey, making it more challenging for these animals to find food. This disruption in feeding patterns can lead to nutritional stress and impact the overall health and survival of marine populations.
The constant exposure to high levels of ocean noise can induce chronic stress in marine animals. Stress can have a range of physiological and behavioral effects, including suppressed immune systems, altered reproductive patterns, and increased vulnerability to diseases. Prolonged exposure to noise pollution can weaken the overall resilience of marine species, making them more susceptible to other environmental stressors and reducing their ability to adapt to changing conditions.
The disruption caused by ocean noise can have broader ecological consequences. Changes in the behavior and distribution of marine species can impact the structure and functioning of marine ecosystems. For example, if certain species avoid noisy areas, it can lead to imbalances in predator-prey relationships and alter the composition of marine communities. These cascading effects can have far-reaching implications for the overall health and stability of marine ecosystems.
The detrimental effects of ocean noise on marine life highlight the urgent need for conservation and mitigation efforts. Protecting marine habitats and implementing measures to reduce noise pollution can help mitigate the impacts on marine species. This includes implementing quieter ship designs, regulating shipping routes to minimize noise in sensitive areas, and promoting sustainable fishing practices that minimize noise disturbance.
Furthermore, addressing the root causes of climate change is crucial for mitigating the spread of ocean noise. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources can help slow down the pace of climate change and alleviate its impacts on marine ecosystems.
While significant progress has been made in understanding the relationship between climate change and ocean noise, further research is needed to fully comprehend the extent of the issue and develop effective strategies for mitigation. Continued monitoring of noise levels in the oceans, studying the specific impacts on different marine species, and raising awareness about the importance of reducing noise pollution are essential steps towards protecting marine life in the face of climate change.
By recognizing the profound effects of climate change on ocean noise and taking proactive measures to address this issue, we can strive towards a more sustainable and harmonious coexistence with the diverse and fragile ecosystems of our oceans.
If you’re wondering where the article came from!
#