Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
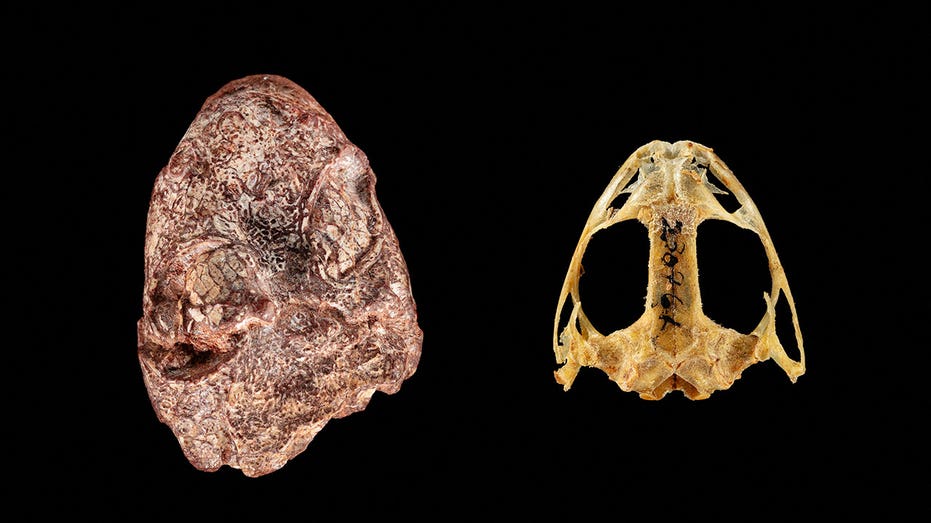
Recent news from Fox News has brought to light a groundbreaking discovery in the field of paleontology – the fossil of Kermitops gracilis, an ancient amphibian believed to be a precursor to modern amphibians. This remarkable finding has provided invaluable insights into the evolution of amphibians and has reshaped our understanding of their origins and development.
One of the significant implications of the Kermitops gracilis fossil discovery is the confirmation of its placement within the ancestral lineage of modern amphibians. Through careful analysis and comparison, researchers have established that Kermitops belonged to a lineage that includes frogs, salamanders, and limbless caecilians. This confirmation sheds light on the existence of a distinct ancestral group that played a crucial role in the evolution of amphibians.
The unique characteristics of the Kermitops skull have provided researchers with valuable insights into the early forms of amphibians. The preserved skull features, such as the rounded snout and the presence of roof-shaped bones, offer clues about the appearance and physiology of this ancient creature. These distinct features also highlight the significant changes that occurred in the skeletal structure of amphibians over time.
The length discrepancy between the front and back of the Kermitops skull suggests the possibility of specialized feeding behaviors. Researchers speculate that the unique skull structure allowed Kermitops to rapidly close its jaws, enabling it to capture fast-moving insect prey. This insight into feeding adaptations provides a glimpse into the ecological niche occupied by Kermitops and its role in the ancient ecosystem.
The discovery of Kermitops challenges the previously held notion of a linear evolutionary trend in modern amphibians. Researchers argue that Kermitops did not follow a clear, step-by-step adaptation to the characteristics seen in modern amphibians. This finding suggests that the evolution of amphibians was more complex and diverse than previously understood, with each lineage developing unique features and adaptations.
The significance of the Kermitops discovery lies in the continuous addition of new fossil data to enhance our understanding of amphibian evolution. Due to the limited fossil record of early amphibians and their ancestors, tracing the origins of modern amphibians has been challenging. However, the unique anatomical structure of Kermitops provides valuable data for unraveling the puzzle of evolution. This emphasizes the ongoing importance of paleontological research and the discovery of new fossil specimens.
The naming of the organism as Kermitops, derived from the iconic character Kermit the Frog, has sparked public interest and created a connection between popular culture and the field of paleontology. This cultural reference has helped generate interest in the importance of understanding evolutionary history and highlights the potential impact of popular culture on public engagement with scientific discoveries and discourse.
The discovery of the Kermitops gracilis fossil has undoubtedly had a profound impact on our understanding of amphibian evolution. From confirming ancestral lineages to providing insights into early amphibian forms and feeding behaviors, this discovery has challenged existing evolutionary trends and emphasized the importance of fossil data. Furthermore, the cultural connections and popular culture references have sparked public interest and increased awareness of the significance of understanding our evolutionary past.
The discovery of the Kermitops gracilis fossil has had a profound impact on the field of paleontology and our understanding of amphibian evolution. This groundbreaking finding has led to several significant effects that have reshaped our knowledge and opened up new avenues of research.
The identification of Kermitops as an ancestor to modern amphibians has prompted a reevaluation of existing evolutionary models. Researchers have had to reconsider the linear progression previously assumed in amphibian evolution. The discovery of Kermitops suggests a more complex and diverse evolutionary path, with different lineages exhibiting unique characteristics and adaptations. This revised understanding of amphibian evolution has the potential to reshape our entire perception of the evolutionary history of these creatures.
The unique characteristics of the Kermitops skull have provided researchers with a wealth of information about early amphibian forms. By studying the preserved skull features, scientists have gained insights into the morphological and physiological traits of ancient amphibians. This knowledge has allowed for a more comprehensive understanding of the diversity and adaptations of early amphibians, filling gaps in our knowledge and painting a clearer picture of their evolutionary journey.
The discovery of Kermitops and its unique feeding adaptations has shed light on the ecological niche occupied by this ancient amphibian. By studying the length discrepancy in the skull, researchers have hypothesized that Kermitops had specialized feeding behaviors, enabling it to capture fast-moving insect prey. This insight into the feeding ecology of Kermitops provides a glimpse into the ancient ecosystem and the role this species played within it.
The Kermitops gracilis fossil discovery has sparked renewed interest and enthusiasm in the field of paleontology. Researchers and scientists are now motivated to conduct further studies to uncover additional fossils and gather more data on early amphibians and their evolutionary history. This increased focus on research will contribute to a deeper understanding of amphibian evolution and may lead to future discoveries that could revolutionize our knowledge of this ancient group of organisms.
The cultural connection between the name “Kermitops” and the popular character Kermit the Frog has captured the attention of the public. This unique association has sparked interest and curiosity among individuals who may not have previously been engaged with paleontological research. The public’s increased interest in the field of paleontology can lead to a greater appreciation for scientific discoveries and a broader understanding of the importance of studying our evolutionary past.
The effects of the Kermitops gracilis fossil discovery have been far-reaching, impacting our understanding of amphibian evolution, prompting revisions to existing models, and stimulating further research. By enhancing our knowledge of early amphibian forms and their ecological adaptations, this discovery has provided valuable insights into the ancient world and the evolutionary processes that have shaped life on Earth.
If you’re wondering where the article came from!
#