Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
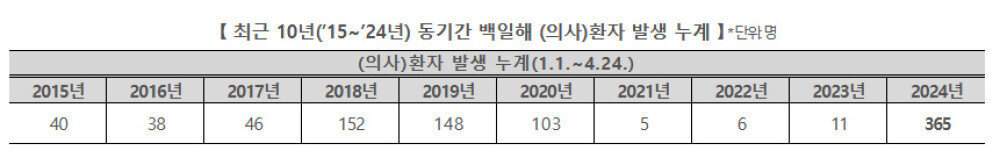
The recent surge in 백일해 (whooping cough) cases in South Korea, particularly within educational facilities, can be attributed to several interconnected causes. These causes have contributed to a significant increase in the number of reported cases over the past 10 years, impacting public health and the education system in the country.
One of the primary causes of the surge in 백일해 cases is a decline in vaccination rates. Vaccination plays a crucial role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases, including 백일해. Factors such as vaccine hesitancy, misinformation, and lack of access to healthcare services have contributed to lower vaccination rates, leaving a larger population susceptible to the disease.
Over time, the immunity provided by previous vaccinations can wane, making individuals more susceptible to 백일해. This waning immunity can be attributed to various factors, including changes in the circulating strains of the bacteria that causes the disease. As a result, even individuals who were previously vaccinated may be at risk of contracting and spreading the infection.
The interconnectedness of the world through travel and globalization has facilitated the spread of infectious diseases, including 백일해. As people travel internationally, they can unknowingly carry the bacteria and introduce it to new populations. This increased movement of people has contributed to the wider dissemination of the disease, leading to a higher number of cases in South Korea.
Herd immunity refers to the protection provided to a population when a significant portion of individuals are immune to a disease. As vaccination rates decline and waning immunity becomes more prevalent, the overall level of herd immunity decreases. This reduction in herd immunity leaves vulnerable populations, such as young children and individuals with compromised immune systems, at a higher risk of contracting 백일해.
The accuracy of reported 백일해 cases is influenced by the effectiveness of disease surveillance and reporting systems. Inadequate surveillance and reporting can lead to underestimation of the true number of cases, hindering the implementation of timely preventive measures. Improved surveillance and reporting mechanisms are essential for early detection, effective management, and prevention of further spread.
Educational facilities, such as schools and daycare centers, provide an environment conducive to the spread of infectious diseases. The close proximity of students and limited ventilation can facilitate the transmission of 백일해 from one individual to another. As a result, educational facilities have become hotspots for the transmission and outbreak of the disease.
A lack of awareness about the symptoms, transmission, and preventive measures of 백일해 can contribute to its spread. Insufficient education and information about the disease may lead to delayed diagnosis, inadequate treatment, and ineffective preventive measures. Promoting awareness and providing accurate information about the disease are crucial in controlling its transmission.
Socioeconomic factors, such as poverty and limited access to healthcare, can also contribute to the surge in 백일해 cases. Individuals facing economic challenges may have difficulty accessing healthcare services, including vaccinations and timely medical care. These disparities in healthcare access can exacerbate the spread of infectious diseases, including 백일해, within vulnerable populations.
Understanding the interconnected causes of the surge in 백일해 cases is essential for implementing effective preventive measures and managing the disease. By addressing vaccination rates, promoting awareness, improving disease surveillance, and implementing appropriate preventive measures, it is possible to mitigate the impact of 백일해 and protect public health in South Korea.
The surge in 백일해 (whooping cough) cases in South Korea, particularly within educational facilities, has had significant effects on various aspects of society. These effects span public health, education, and the overall well-being of the population.
The increased number of 백일해 cases has put a strain on the healthcare system in South Korea. Hospitals and clinics have experienced a surge in patient visits, leading to longer wait times and overcrowded facilities. The influx of patients has stretched healthcare resources, including doctors, nurses, and medical equipment, resulting in potential challenges in providing timely and adequate care to all patients.
The outbreak of 백일해 in educational facilities has caused significant disruptions to the education system. Schools and daycare centers have had to implement preventive measures, such as temporary closures and quarantine protocols, to contain the spread of the disease. These measures have resulted in interrupted learning processes, increased student absences, and challenges for teachers in adjusting their lesson plans to accommodate the impact of 백일해 on students’ attendance and academic progress.
The surge in 백일해 cases can have economic consequences at both the individual and societal levels. Parents may need to take time off work to care for their sick children, leading to productivity loss and potential financial strain on families. Additionally, the increased burden on the healthcare system and the demand for diagnostic tests, medications, and vaccines can have financial implications for both individuals and the government.
The rise in 백일해 cases in South Korea has raised concerns globally. Reports from various countries in Europe, as well as other parts of the world, indicate the spread of the disease beyond South Korea’s borders. This global concern emphasizes the need for international cooperation in monitoring and managing the disease. Sharing information and best practices between countries becomes crucial in mitigating the impact of 백일해 on a global scale.
The surge in 백일해 cases highlights the importance of vaccination and preventive measures. Vaccination, particularly among infants and school-aged children, plays a vital role in reducing the spread of the disease and protecting vulnerable populations. Public health authorities emphasize the need for timely and complete vaccination schedules, along with promoting good hygiene practices such as regular handwashing and proper cough etiquette, to prevent 백일해 and other respiratory infections.
The increase in 백일해 cases underscores the importance of public health awareness and preparedness. Enhancing public knowledge about the symptoms, transmission, and preventive measures of 백일해 can empower individuals to take appropriate actions and seek timely medical attention. It also highlights the need for robust disease surveillance systems, effective reporting mechanisms, and coordinated responses to manage outbreaks and prevent further spread.
The surge in 백일해 cases emphasizes the significance of achieving and maintaining herd immunity. By ensuring high vaccination rates and protecting vulnerable populations, such as infants and individuals with compromised immune systems, herd immunity can be strengthened. This collective protection helps reduce the overall burden of 백일해 and prevents its transmission within communities.
The effects of the surge in 백일해 cases are far-reaching, impacting healthcare, education, the economy, and global health concerns. By addressing these effects through proactive measures, including vaccination campaigns, public health awareness programs, and collaborative efforts, it is possible to mitigate the impact of 백일해 and protect the well-being of the population.
If you’re wondering where the article came from!
#